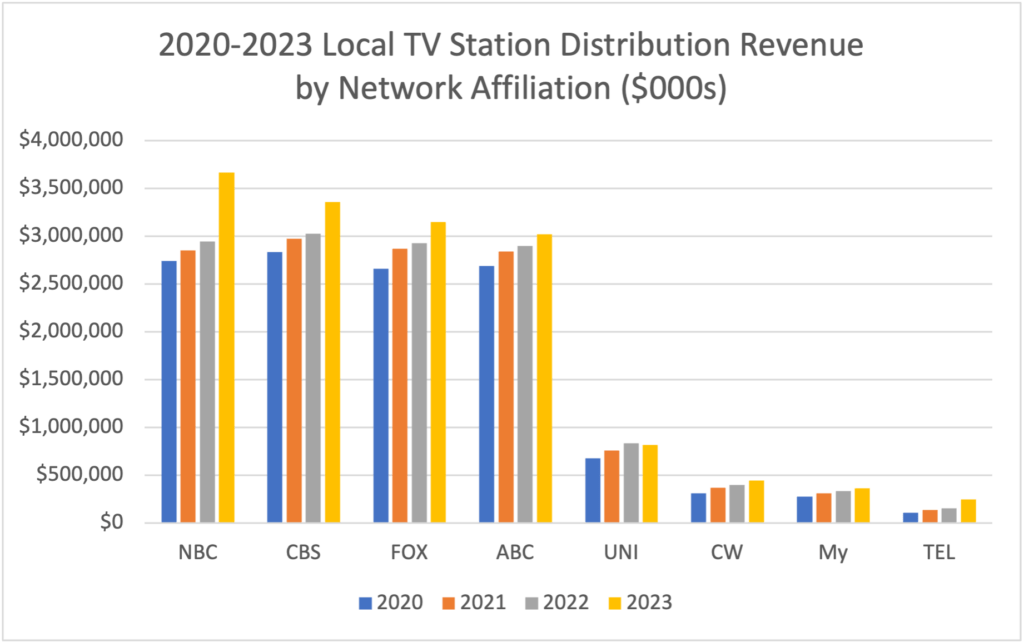
BIA estimates that local TV stations generated $12.3 billion in distribution revenue from MVPDs and vMVPDs in 2020, and this rose 22.5 percent to $15.1 billion by 2023. As shown below, NBC affiliated stations saw the largest increase in distribution revenue in this period, followed by CBS, FOX, and ABC. Broadcasters often negotiate both financial and non-financial terms such as including carriage of diginets.
Local TV stations typically have 3-5 year agreements with MVPDs and vMVPDs for distribution of their over-the-air signals (i.e., “retransmission consent”). While station groups largely negotiate their own distribution agreements with MVPDs, networks have led the way in setting distribution terms with vMVPDs. This distribution is split between stations and their affiliated networks (i.e., reverse comp) with networks getting more than half of this revenue.
Looking ahead beyond 2023, the local TV industry has come to rely on these distribution revenues but the dynamics are in flux. BIA’s calculation and forecasts of retransmission fees are based on the overall and expected growth in:
- Audience ratings
- Television households
- Cable penetration rates
- Fees local stations are receiving from cable and satellite delivery systems
- Fees local stations are paying parent networks for their share of these revenues
- Amounts received by non-top four affiliates (CW, MY, and Univision).
In a world with growing segments of homes that are cord-cutters and cord nevers with a transition to CTV/OTT streaming video services, the economics of retransmission consent are changing as MVPDs see video subscriber losses along with the associated revenues from which distribution fees can be paid. MVPDs themselves are making adjustments by moving towards offering their own streaming services served to their growing ranks of broadband customers versus their traditional cable households.
For example, Charter and Comcast are replacing old school set-top boxes with the Xumo Stream Box offering live channels and streaming services and platforms including Hulu, Disney+, Netflix, and Max. CBS’ move of Seal Team from the broadcast network to its Paramount+ platform is one such example. Linear audience ratings are smaller. And premium content is starting to move from over-the-air to streaming platforms to increase recruitment and retention in the FAST, AVOD, and SVOD services where audience and revenue is more promising.
What does the future hold for local TV stations who have come to count on this distribution revenue which, in some cases, exceeds their advertising revenue?
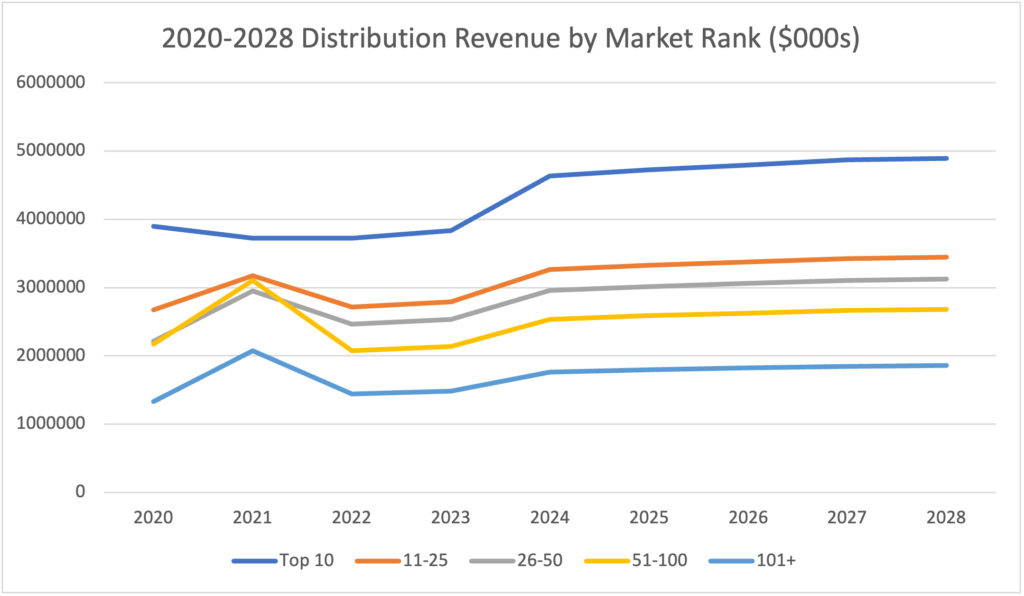
BIA’s latest forecast for local TV station vMVPD/MVPD distribution revenue shows growth from 2023 but an overall flattening in the 2024-2028 period. Of the total amount of distribution revenue in the 2020-2028 period, the Top 25 TV Markets account for over half of the local TV station revenue from multichannel video providers. The Top 10 markets generate 29.9 percent of the total and Markets 11-25 get 21.6 percent.
To learn more about local TV station distribution revenue by station, group, year, market, etc., BIA offers its MAPro industry database with these data and hundreds of other fields on each local TV station.
BIA will be sharing more data and insights about the local TV industry’s financial outlook and strategies October 9th at NAB New York as part of TV NewsCheck’s Local TV Strategies: How to Thrive in 2025 conference.

